A roadmap for the National Steering Committee for the public finance reform strategy
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) experienced an economic slowdown in 2023, with growth estimated at 8.6%, down from 8.9% the previous year. This slowdown is mainly attributed to several factors:
- Declining global demand for mining products, particularly cobalt, prices of which have plummeted.
- Rampant inflation, reaching 23.8% in 2023, compared with 13.1% the previous year, which has had a significant impact on the purchasing power of the Congolese.
- Pressure on public finances due to increased spending on security and the general elections scheduled for December 2023, leading to a deterioration in the budget deficit to 1.3% of GDP.
- Persistent political instability and security tensions in the east of the country, making it difficult to implement the structural reforms needed to attract foreign investment.
However, forecasts for 2024 indicated that growth could stabilise at around 6%, supported by the mining sector, but this recovery remains fragile and dependent on fluctuations in world commodity prices.
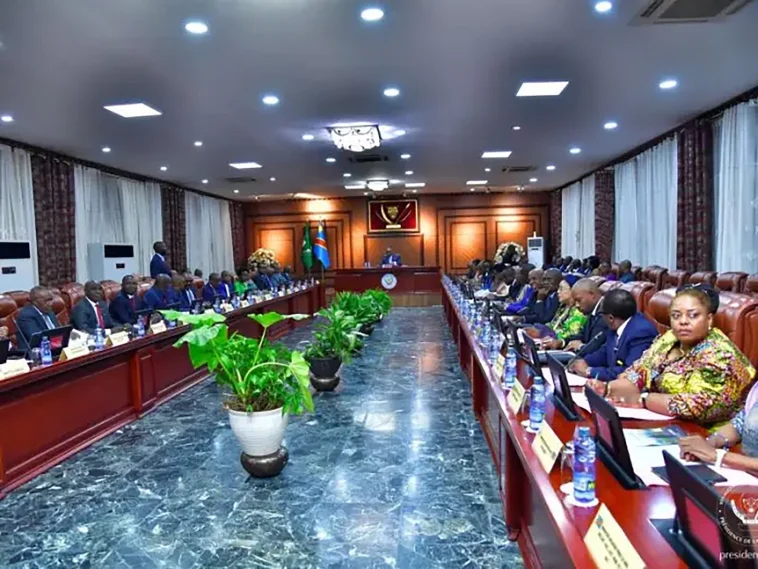
In November 2024, the Democratic Republic of Congo continued its economic reform drive by putting forward a Public Finance Reform Strategy for the period 2022-2028. The Deputy Minister of Finance, O’Neige N’sele, detailed the content of this ambitious programme, accompanied by an updated operational plan for 2025-2027. ‘Following a realistic approach, this plan prioritises the areas, measures and actions for reform, as well as the activities to be undertaken over the medium term’, she explained. I
The plan is a strategic document that focuses on targeted actions capable of having an immediate impact on public finances.
Strategic priorities for modernised management
The reform plan is based on seven fundamental strategic axes. These include
- Budgetary reform: rationalising resources and strengthening fiscal discipline.
- Tax policy and the capacity of tax administrations: increasing internal revenues.
- Public expenditure management: better control of financial flows.
- Digitisation of public finances: introducing modern tools for greater transparency.
Financial decentralisation is also taken into account.
Financial decentralisation is also taken into account, with a particular effort to strengthen financial management at provincial and local level.
The three-year plan for 2025-2027 identifies four priority measures, detailed in a matrix presented to members of the government. This matrix now forms the roadmap for the National Steering Committee for the Public Finance Reform Strategy, which is responsible for monitoring implementation at regular meetings chaired by the Prime Minister.
Continuity in the reform vision
The new programme aims to strengthen economic fundamentals and modernise the management of public finances, while relying on concrete initiatives and rigorous monitoring tools.